Function: Data Logging
Reliable basis for data-driven decisions
This chapter explains an essential function of the DO-1 - Data Logging. The creation of logs makes it possible to record certain events or actions, which can be helpful for fault diagnosis, among other things. The saved data can then be viewed and downloaded for further processing.
Configuration – Add and edit data log tasks
Clicking on Configuration opens the main page of this function. Once log tasks have been created, they appear in a list view. The tasks can be subsequently edited at any time.
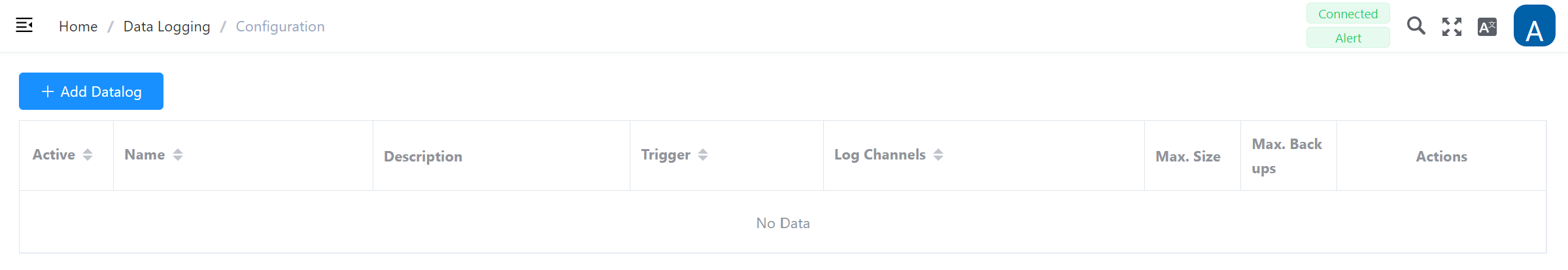
The following actions are available for log tasks that have been created:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Edit | Opens the data entry for editing the settings |
| Delete | Removes the order from the system. (A warning notice must also be confirmed) |
Adding a job for a data log
Click on Add data log to open another window with the following entry mask.
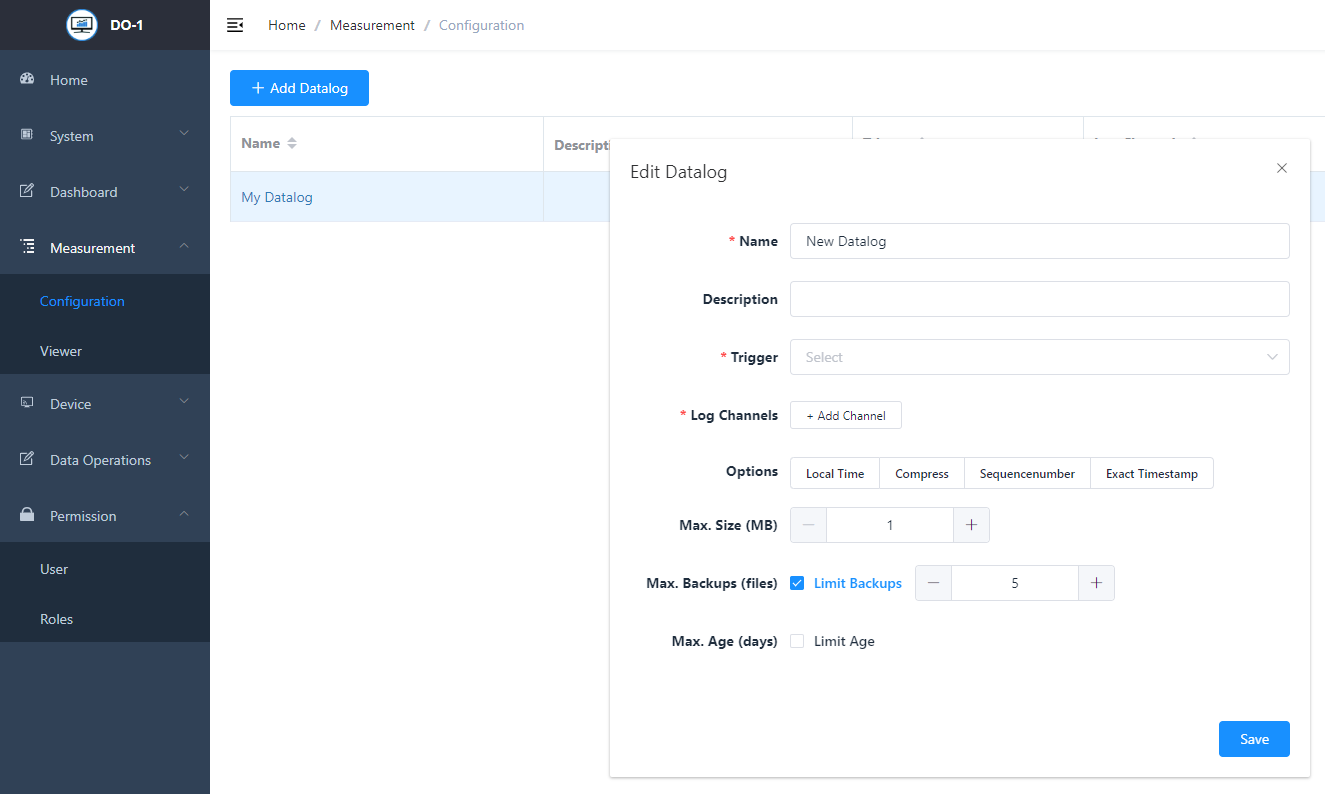
Edit data log - Settings
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name * | Individual; Assignment of a name for the data log |
| Description | Optional; any description can be added here, including more detailed information about the data log. |
| Trigger * | Specify what exactly should trigger the calculation. Several areas are available for selection via a drop-down menu: System based: Bus updated, Bus failure, Device updated, Register updated, Buffer full. If selected, the respective location (bus, device, register) must be selected in an additional field. Data automized: Calculation completed, alarm triggered, Alarm cleared, Alert triggered or cleared. If selected, the respective calculation or alarm must be selected in another field. Time based: Runs every…; Specify frequency and time of day (dd, hh:mm:ms) when the calculation is to run. Runs at…; Specify exact timing (seconds, minutes, hours, day, month) for the calculation. |
| Log channels * | Add the corresponding location channels. This is necessary for the trigger to work. You can add several channels via Add channel |
| Options | Several options can be added to the order to obtain detailed information that may be necessary for the evaluation of the data. Local time: The time is logged in the local time zone instead of UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) Compression: Sends log-file(s) to a gzip compressed file format Sequence number: In addition to the measured value, the sequence number of the measured value is logged. Exact timestamp: Adds the exact time an event was recorded to the log-file. |
| Max. Size (MB) | Define the maximum file size in megabytes |
| Max. backup (files) | Define the maximum backup copies |
| Max. Age (days) | Limitation possible; if you activate the limitation, a limitation of the maximum days must be entered. |
Note: All fields marked with * are mandatory.
Example for a data log task:
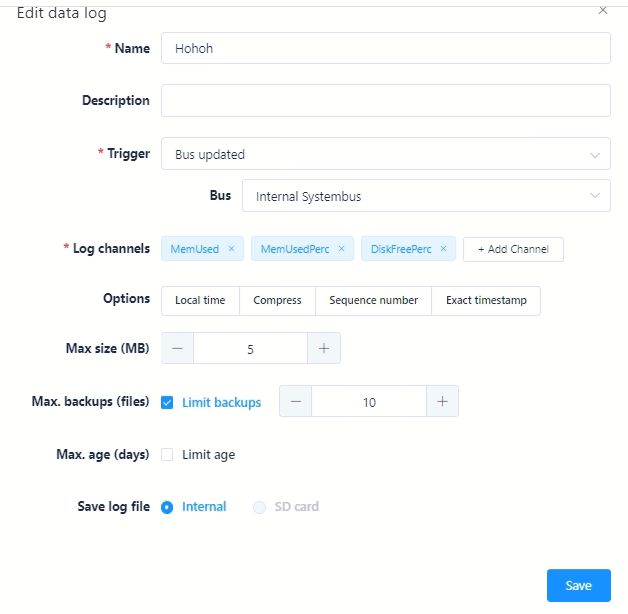
Click on Save to secure all entries made for the data logging task.
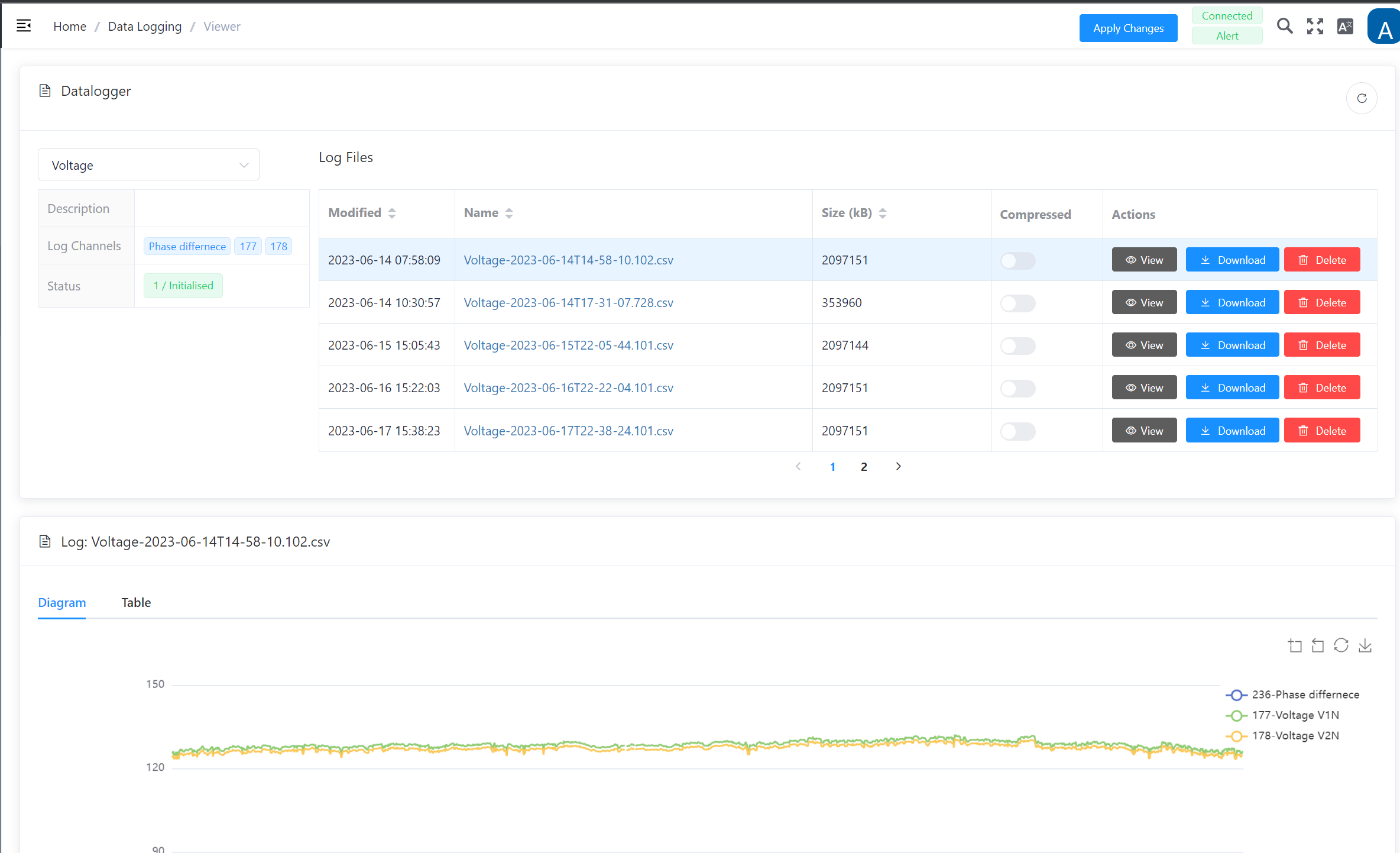
Viewer – Access the saved data logs
The Viewer provides access to the saved data for the individual jobs. Use the drop-down menu on the top left to select the relevant job and, in addition to the general information (description, channels and status), all log files that have already been created are displayed chronologically.
The following actions are available here:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| View | Displays a corresponding graphic in the lower screen |
| Download | Downloads the data file in .csv (comma-separated values) format |
| Delete | Allows the data file to be removed |
Example of a data log overview: